
ROXAS BOULEVARD UNDERWATER A storm surge on Manila Bay generated by Typhoon “Pedring” slams into Roxas Boulevard, sending jets of water upward and submerging the boulevard. It was high tide and Pedring enhanced the southwest monsoon. Some areas along the bay suffered their worst flooding in decades.
(Editor’s Note: A name familiar to people matters a lot. As Supertyphoon “Yolanda” has shown, it is a matter of life and death. Thousands of people in Leyte and Samar died when a wall of water slammed into coastal communities in Eastern Visayas on November 8.
Despite warnings from the authorities that Yolanda would bring a storm surge of 5 to 7 meters, many people did not leave their homes along the shore. The reason: they did not know what a storm surge was.
A survivor in Tacloban said his loved ones would have been saved had the government warned that tsunami-like waves would hit the city.
So choosing a term that would mean a storm surge is of utmost importance. So far, the proposed terms for storm surges include “tsu-balod,” “tsu-alon,” “silakbô,” “daluyong,” “humbak” and “Tacloban.”)
At Pinatubo during the 1990s, we inadvertently stumbled upon one of our most valuable educational tools when we introduced “lahar” to the people threatened by that phenomenon.
It was a real word, commonly used in Indonesia, and already had been adopted in scientific circles after we started using it in our scientific papers about our work at Mayon.
But it was new to people around Pinatubo, whose attention and interest were aroused when they first heard it. And when they would eagerly ask, “What does lahar mean?” the learning process would begin naturally.
Filipino term
So we do need a good Filipino word. Unfortunately, tsu-alon or tsu-balod is not very appropriate.
Tsunami comes from the Japanese “tsu” meaning “harbor” and “nami” meaning “wave.” So tsu-alon would be a “Japalog” (Japanese-Tagalog) word that would back-translate into tsunami in pure Japanese.
In naming storm surge in Filipino, we must get away entirely from tsunami or anything like the term. This is because tsunamis and storm surges differ in very important ways, and conflating them can create serious problems.
Tsunamis are generated by four different and unpredictable triggers: Undersea volcanic eruptions; Earthquakes; Landslides; and much more rarely, by large meteorite impact on the ocean.
DEVASTATION A part of Tacloban City before and after a six-meter surge spawned by Supertyphoon “Yolanda” destroyed it. Two huge ships slammed into the community, killing residents.
Very little warning
Tsunamis can come with very little warning.
For example, the March 11, 2011 tsunami that devastated Fukushima occurred only about an hour after the Tohoku earthquake.
People know about the very short lead times of tsunamis and if told a tsunami is coming, they can easily panic, which by itself can be lethal.
On December 1, residents of Iloilo, Antique and Capiz were needlessly panicked by a false tsunami alarm. This happened again in Basey, Samar, on Dec. 12. This is because people think storm surges and tsunamis are the same thing.
Days of lead time
Unlike tsunamis, thank goodness, storm surges are preceded by several days of lead time, during which the approaching typhoon can be closely monitored and orderly preparations can be made to evacuate the people in harm’s way, and minimize both panic and the impact itself.
Mahar Lagmay of Project Noah (Nationwide Operational Assessment of Hazards) and I have also been looking for a Filipino word for storm surge. We were glad to learn that historian Jaime Tiongson of Bahay Saliksikan ng Kasaysayan, had put forward “humbak.”
Serious business
But it turns out to be even more inappropriate than tsu-alon—humorously so, as I will show.
Creating or choosing a Filipino term is serious business. We want it to be new to arouse interest and to sound like something serious, a hazard.
Linguistic heritage
But we must also be respectful of the language, protective of our linguistic heritage. It should be a real word, preferably one that currently is rarely used, so it is new to most people.
Finally, it must be faithful to the nature of the thing we are defining.
Fr. English’s dictionaries
To begin a serious search for a proper word, I consulted the very best English-Tagalog and Tagalog-English dictionaries available—those of Fr. Leo English, a Redemptorist from Australia.
English began compiling his Tagalog-English and English-Tagalog dictionaries during World War II in Los Baños, Laguna, where he was a prisoner of the Japanese.
It took him 30 years to complete them while he lived with and ministered to Batangueños. These superb lexicons give examples of proper usage. No other dictionaries are as complete. His English-Tagalog Dictionary boasts 1,211 pages; his Tagalog-English Dictionary is 1,583 pages long.
In 1960, when Jose Villa Panganiban, director of the Institute of National Language (INL) first saw English’s Tagalog-English dictionary in manuscript, the INL English-Tagalog Dictionary had just been published.
Panganiban, however, concluded that English’s work was more complete and displayed “profound scholarship and he encouraged the priest to continue his work.
The only edition of the INL English-Tagalog Dictionary was its run of 13,000 copies in 1960. Effectively, INL yielded the field to English, whose English-Tagalog Dictionary was first published by Kalayaan Press in 1977.
The Australian government has subsidized many subsequent printings. My copy is from the 19th printing in 1994.
English’s Tagalog-English Dictionary took longer to publish, also by Kalayaan Press. Its first printing was in 1986 and my copy is of the 9th printing, dated 1994.
‘Humbak,’ ‘daluyong’
In that lexicon, humbak is defined as “trough between waves.” Its other meaning is “depression in a surface.”
English gives humbak as a synonym. But he separately translated humbak in its own right as an adjective, meaning “hollow,” “sunken,” or “concave,” as in reference to cheeks hollowed by sleeplessness: Humbak ang mga pisngi niya dahil sa kapupuyat. This enforces the fact that humbak is the exact opposite of “wave”!
This has been corroborated by National Artist Virgilio Almario (“Finding a Filipino word for storm surge: ‘Daluyong’ or ‘humbak?’” by Ira Pedrasa, ABS-CBNnews.com, 11/18/2013): “Ang humbak ay pagitan ng dalawang alon. Ito yung cavity na tinatawag. Walang laman.”
So how did English translate the noun “surge” into Tagalog? Turning to his English-Tagalog Dictionary: “surge: (2) n. a wave; a sweep or rush of waves: Paggulong ng alon, daluyong. The surge of the sea: Ang daluyong ng dagat.”
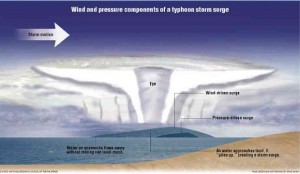
Can daluyong serve? Unfortunately, the term is widely understood to simply mean “large ocean wave” and storm surges are more complicated than typical water waves that repeatedly arrive every few seconds.
Manila Bay
To learn the difference between a storm surge and storm waves, video footage of the surge and storm waves in Manila Bay generated by Typhoon “Pedring” on Sept. 27, 2011 is very instructive.
These are widely available on the Internet: youtube.com/watch?v=KVqOVR9lytk and youtube.com/watch?v=UlhncBQE8-A.
Most viewers mistakenly think that the gigantic storm waves, following each other every several seconds, smashing against the breakwater and sending huge plumes up higher than the tallest coconut trees along Roxas Boulevard, are separate storm surges, but they are not.
36-hour ‘Pedring’ surge
A single surge takes hours and even days to pass, depending on the motion and duration of the generating typhoon and its timing with respect to the tides.
Project Noah has determined that the Pedring surge lasted about 36 hours and was only 1.8 meters high. During the short periods of the footage, the surge already raised the water level and flooded inland to inundate the US Embassy and areas beyond it. But its height doesn’t change while we watch.
What inspires our awe are not storm surges. They are regular storm waves riding atop the storm surge.
Silakbô
Continuing English’s definition of surge: (3) something like a wave: “Silakbô.” “Bugso.” A surge of anger: “Silakbô ng galit.”
Bugso is already widely used by Pagasa (Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration) in reference to cloudbursts and thundershowers, “pabugso-bugso.” This leaves silakbô.
English’s example of surging anger suggests violence and the stress on the last syllable may also euphonically suggest suddenness.
So how about silakbô ng bagyo? That would literally mean “storm surge.” With continued use, silakbô alone would eventually suffice.
(Kelvin S. Rodolfo is professor emeritus at the Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences, University of Illinois in Chicago and is corresponding member of the National Academy of Science and Technology.)

